Reserve museum «Tanbaly»
Settlements


Settlements in Tanbaly are located exclusively in the mountainous part of the tract. In the conditions of hilly terrain (melkosopochnik), settlements occupy a small area from 300 to 1200 sq. m. and are located in various geomorphological conditions: on wide areas of valleys, gentle slopes of small gorges (sai) or on elevated areas of the so-called "hanging" valleys. Despite the differences in topography, all sites have a southern, south-western or south-eastern exposure. The presence on most settlements of the remains of stationary buildings (dwellings, cattle pens), as well as the specified location features indicate their long-term, mainly seasonal (in winter), use by ancient pastoralists of Tanbaly.
Many of the famous settlements of Tanbaly are multi-layered monuments containing cultural remains of several historical eras. Excavations were carried out only at two settlements - Tanbaly I and V. The most important stratigraphic data were obtained at the settlement of Tanbaly I, where the cultural strata of four historical periods were revealed.
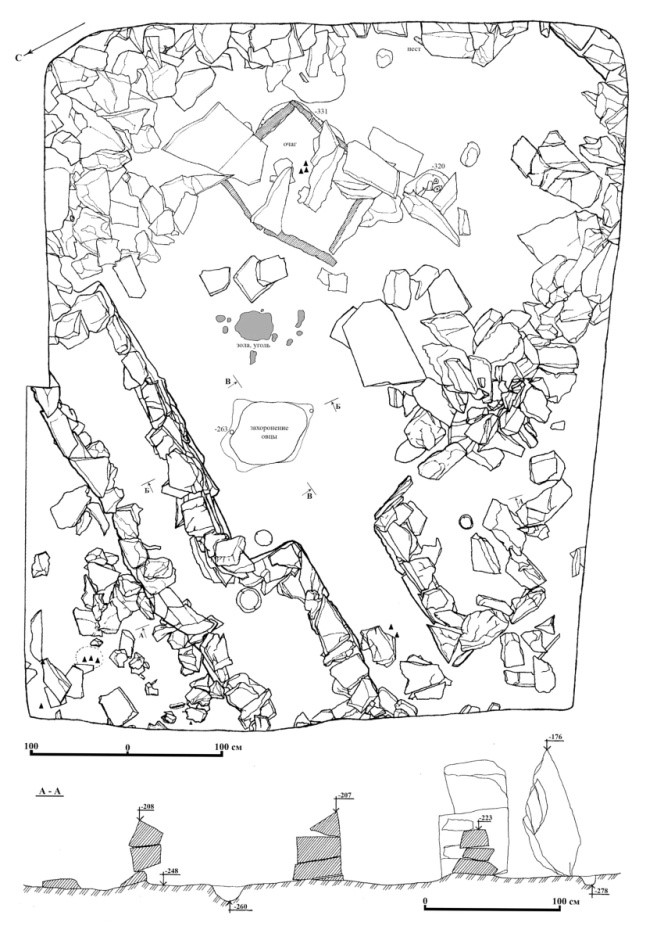
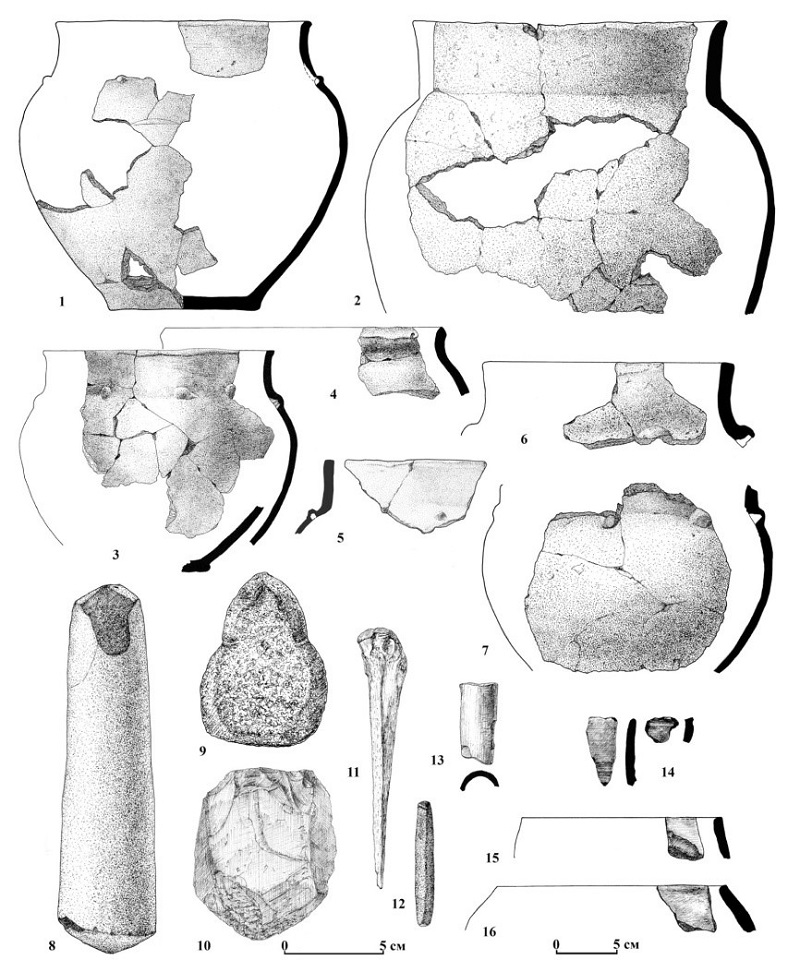
The settlement of Tanbaly I; (N 43º4748,3E 075º3147,1) is located in an intermountain valley developed on the southern slope of the ridge forming the left side of the western tributary of the Tanbaly River. The remains of four ring-shaped stone structures have been preserved on the surface. Lifting material includes animal bones, fragments of ceramics, bone products and fragments of metal products.
At a depth of 2.8-3.2 m, a well-preserved stone foundation of a late Bronze dwelling (XII-X centuries BC according to a calibrated date) with a floor hearth and a ritual burial of a domestic sheep under the floor was found; the ceramic complex is represented by Dongal-type forms and fragments of easel and black-flattened imported dishes. Above were the remains of stone structures of the Early Iron age (VI/V - IV centuries BC and II century BC - I century AD according to three calibrated dates), overlain by two layers of fire, as well as the Late Middle Ages (XVI-XVII centuries) and the ethnographic period (the turn of the XIX-XX centuries). For various layers of the settlement, more than ten calibrated dates were obtained by the 14C and EPR method.
Excavations at the settlement were carried out by the Tanbalian Archaeological detachment of the IA NAS RK in 1992 and the NIPI of monuments of material culture in 1998-2000 under the leadership of A.E.Rogozhinsky. The cultural remains of four chronological periods are revealed: the Bronze Age, the Early Iron Age, the Late Middle Ages and the end of the XIX century. The special significance of the monument is determined by the presence of the remains of residential stationary and outbuildings, on some stones of which petroglyphs were found.
Petroglyphs above the settlement
Rock carvings are located on the slope and ridge of the hill above the settlement. There are about 100 images dating from the Bronze Age, the Early Iron Age, the Middle Ages.
- The settlement of Tamgaly V(N 43º4733,4E 075º3303,12) occupies an extended area at the mouth of the erosion valley, on the left bank of the dry riverbed. The remains of two or three stone structures overlain by deluvial-proluvial deposits have been preserved on the surface. In 1992, a stratigraphic pit was passed at the settlement (TAO IA NAS RK, G.S.Dzhumabekova, A.E.Rogozhinsky), a cultural layer and the remains of stone structures were identified. Dating– theEarly Iron Age.
Petroglyphs near the settlement
The petroglyphs are located on the southern slope of the hill on the left side of the gorge, above the settlement of Tamgaly V. There are more than 150 images. Individual animal images may date back to the Bronze Age. Petroglyphs of the early Iron Age prevail numerically: images of animals in the Saka animal style, scenes of persecution and hunting of wild goats and deer, an uninterpreted image similar to images of labyrinths.

 3D Tour of Tanbaly
3D Tour of Tanbaly
